```html
Inside the Power Units: What Engines Do Formula 1 Cars Use?
Imagine the roar of the crowd, the blur of colors, and the sheer adrenaline as Formula 1 cars tear around the track at breakneck speeds. At the heart of this incredible spectacle lies a marvel of engineering: the Formula 1 engine. But what exactlyarethese engines? And what makes them so special? Understanding the intricate power units of these racing machines is not just fascinating, it's crucial for any aspiring driver or motorsport enthusiast seeking to understand the pinnacle of automotive performance. This article will dive deep into the world of F1 engines, exploring their design, technology, and the regulations that govern them.
The Evolution of Formula 1 Engines: A Historical Overview
Formula 1 engine regulations have undergone significant transformations throughout the sport's history, reflecting advancements in technology and the evolving priorities of the FIA (Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile), the governing body. From massive, naturally aspirated engines to the sophisticated hybrid power units of today, the journey has been one of constant innovation and adaptation.
In the early days, engines were large and relatively simple, focusing on raw power. Over time, turbocharging became prominent, leading to some of the most powerful engines ever seen in F1. However, concerns over safety and fuel consumption led to restrictions and eventual bans on turbocharging, paving the way for the return of naturally aspirated engines, often with displacement limits.
The modern era has seen a shift towards sustainability and efficiency, resulting in the introduction of hybrid power units. These units combine internal combustion engines with electrical components, offering a blend of power and fuel economy.
Decoding the Modern F1 Power Unit: A Technical Deep Dive
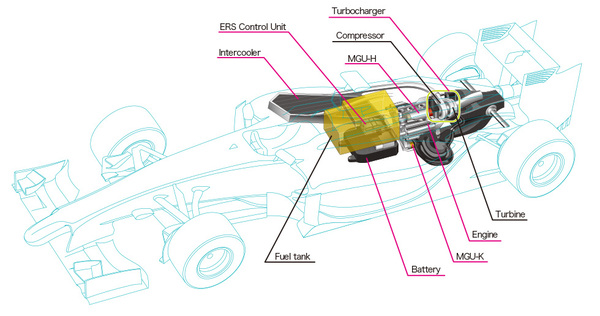
Today's Formula 1 cars utilize highly sophisticated power units, far removed from the simpler engines of the past. These units are not just engines in the traditional sense but complex systems designed for optimal performance and efficiency under stringent regulations.
The core of the power unit is a 1.6-liter turbocharged V6 internal combustion engine (ICE). This engine is limited to 15,000 RPM and is designed to extract maximum power from a relatively small displacement. The turbocharger, a crucial component, forces more air into the engine, significantly boosting its power output.
Beyond the ICE, the power unit incorporates several electrical components. The Motor Generator Unit – Kinetic (MGU-K) recovers energy during braking and converts it into electrical power, which can then be deployed to provide extra acceleration. The Motor Generator Unit – Heat (MGU-H) recovers energy from the exhaust gases and converts it into electrical energy, further enhancing efficiency. These electrical systems contribute significantly to the overall power output and fuel economy of the car.
The Energy Store (ES) is essentially a battery pack that stores the electrical energy recovered by the MGU-K and MGU-H. This stored energy can then be deployed by the MGU-K to provide a boost in power when needed. The Control Electronics (CE) manage the complex interplay between all the components of the power unit, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding the Intricacies of MGU-K and MGU-H
The MGU-K and MGU-H are integral to the hybrid system of a modern Formula 1 power unit. Their function and interaction are central to the efficiency and performance of the car.
The MGU-K (Motor Generator Unit - Kinetic) is connected to the drivetrain and acts as a generator during braking. When the driver applies the brakes, the MGU-K converts the kinetic energy into electrical energy, which is then stored in the Energy Store (ES). During acceleration, the MGU-K can act as a motor, deploying the stored electrical energy to provide an extra boost of power to the wheels.
The MGU-H (Motor Generator Unit - Heat) is connected to the turbocharger. It recovers energy from the exhaust gases, which would otherwise be wasted. The MGU-H converts this heat energy into electrical energy, which can be used to either charge the Energy Store (ES) or directly power the MGU-K, reducing turbo lag and improving throttle response. The MGU-H allows for much more efficient energy usage, playing a crucial role in improving fuel economy.
Fuel and Oil: The Lifeblood of F1 Engines
The fuel and oil used in Formula 1 engines are not just ordinary substances; they are carefully formulated blends designed to maximize performance and protect the engine under extreme conditions.
F1 fuel is subject to strict regulations, ensuring that it is similar to commercially available gasoline. However, subtle differences in composition and additives can have a significant impact on engine performance. Teams work closely with fuel suppliers to develop custom blends that optimize combustion and power output. While explicitly engineered for maximum power, advances in fuel development also contribute to improving MPG and implementing eco-friendly driving habits. Fuel economy tips and efforts to reduce carbon footprint are often tied to ongoing research into more efficient fuel formulations.
The oil used in F1 engines must also withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. It plays a crucial role in lubricating and cooling the engine components, preventing wear and tear. Oil suppliers develop specialized formulations that minimize friction and maximize engine protection.
Regulations and Restrictions: Governing F1 Engine Development
The FIA imposes strict regulations on Formula 1 engines, aiming to control costs, promote competition, and ensure safety. These regulations cover various aspects of engine design, performance, and usage.
Engine displacement, RPM limits, and fuel flow rates are all tightly regulated. The number of power unit components that each team can use per season is also restricted, encouraging reliability and efficient usage. These restrictions are in place to prevent teams from spending excessive amounts of money on engine development and to create a more level playing field.
Changes to the regulations are frequently introduced to address emerging issues or to promote specific goals. For example, regulations may be adjusted to encourage greater fuel efficiency or to limit the performance gap between different engine manufacturers. These constant adjustments contribute to the ongoing evolution of Formula 1 engines.
The Future of F1 Power Units: A Glimpse Ahead
The future of Formula 1 power units is focused on sustainability and efficiency. The sport is committed to reducing its carbon footprint and developing technologies that are relevant to the wider automotive industry.
Future regulations are expected to promote the use of sustainable fuels and increase the role of electrical power. Hybrid technology is likely to become even more prominent, with the potential for more powerful and efficient electric motors. There is also ongoing research into alternative engine technologies, such as hydrogen combustion, which could play a role in the future of Formula 1.
The long-term goal is to develop power units that are not only powerful and efficient but also environmentally friendly. This will ensure that Formula 1 remains at the forefront of automotive technology while contributing to a more sustainable future.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about F1 Engines
What is the lifespan of a Formula 1 engine?
Due to the extreme stress and performance demands, F1 engines have a relatively short lifespan. Teams are limited in the number of power unit components they can use per season, typically around 3-4 engines, which are strategically deployed to maximize performance and reliability.
How much horsepower does a Formula 1 engine produce?
Modern F1 power units produce around 1000 horsepower, combining the output of the internal combustion engine and the electrical components (MGU-K and MGU-H).
Why are F1 engines so small compared to road car engines?
The 1.6-liter displacement limit is a result of regulations designed to control power and promote efficiency. By forcing engineers to extract maximum power from a small engine, it encourages innovation and technological advancement.
Can Formula 1 technology be applied to road cars?
Yes, many technologies developed in Formula 1 eventually find their way into road cars. Examples include advanced materials, fuel injection systems, and hybrid technology. F1 serves as a testing ground for cutting-edge automotive innovations.
How does the sound of an F1 engine compare to other racing engines?
The sound of an F1 engine is unique due to its high RPM and the presence of a turbocharger. The high-pitched whine of the engine combined with the whoosh of the turbocharger creates a distinctive and recognizable sound.
What happens to the used F1 engines after a race?
Used F1 engines undergo thorough inspection and analysis. Components that are still within their lifespan may be reused, while others are retired. Data gathered from these engines helps engineers to improve future designs and performance.
In conclusion, Formula 1 engines, or rather, power units, represent the pinnacle of automotive engineering. They are complex systems designed for maximum performance and efficiency under incredibly stringent regulations. The continuous pursuit of innovation in F1 not only pushes the boundaries of what's possible in motorsport but also drives advancements that ultimately benefit the wider automotive industry. So, the next time you hear that roar, remember the intricate dance of engineering brilliance happening under the hood, constantly evolving and pushing the limits of speed and efficiency.
```

Posting Komentar